liuyazong.github.io
Spring Boot项目的启动流程
文章主要从以下三个方面来分析Spring Boot项目的启动流程
- SpringApplication的创建及run方法执行
- 配置的读取,如application.yml/application.properties等
- component scan的实现,如常见的注解Service、Component、Autowired等
- bean的实例化及初始化
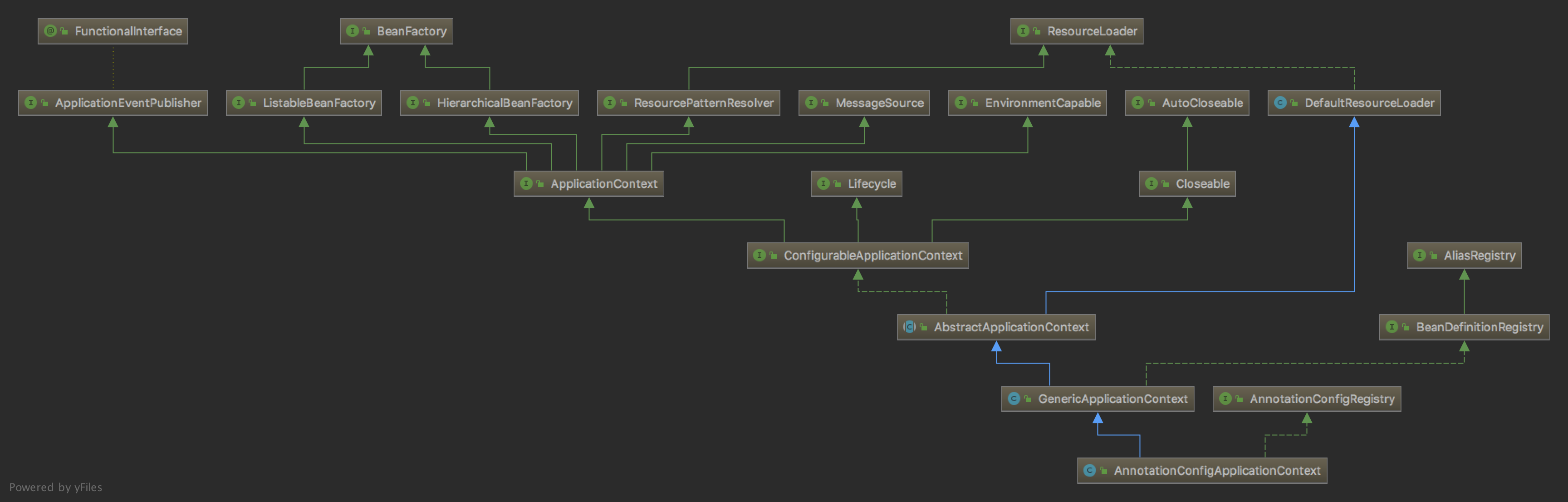
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承结构
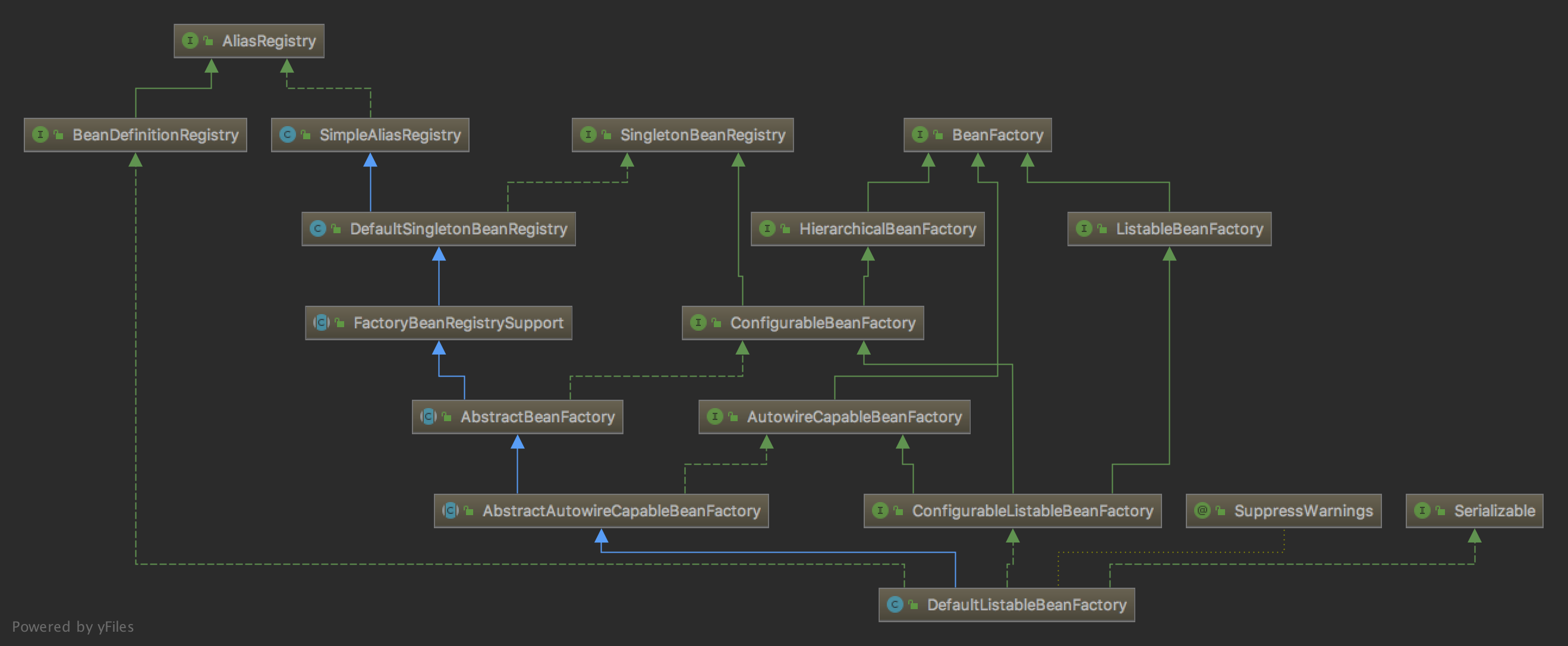
DefaultListableBeanFactory继承结构
一般情况下,创建下面这样一个类,添加Spring Boot的jar包就可以启动一个Spring Boot项目了。我们的分析也将从这里开始。
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication
自动配置
@SpringBootApplication
Spring Boot应用启动时,会处理这个注解。
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* 排除自动配置
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* 排除自动配置
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* 需要扫描的包
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* 需要扫描的包
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* 排除自动配置
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* 排除自动配置
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
public @interface Import {
/**
* {@link Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector}, {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}
* or regular component classes to import.
*/
Class<?>[] value();
}
这里使用@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)导入了一个类AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这个类是DeferredImportSelector的实现类,也是ImportSelector的实现。
Spring在处理@Import注解时,如果它导入的是ImportSelector实现类,则会调用它的selectImports方法。
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的selectImports方法从spring.factories文件加载key为org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的属性,然后将这个属性的值作为配置类进行处理。
自动配置就是这么实现的。
而当@Import的是ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现类时,则会调用它的registerBeanDefinitions方法。
@ComponentScan、@ComponentScans。
SpringApplication构造器
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//为primarySources属性赋值
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//确定web app的类型,REACTIVE、NONE、SERVLET
//如果当前classpath下有org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler,并且没有org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet和org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer,则为REACTIVE
//如果当前classpath下没有javax.servlet.Servlet或者org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,则为NONE
//否则,为SERVLET
//由于引入了依赖spring-boot-starter-web,所以此处为SERVLET
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//从spring.factories加载并实例化所有ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//从spring.factories加载并实例化所有ApplicationListener的实现类
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//确定调用main方法的那个类,目前是MainApp类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
ApplicationContextInitializer
使用SpringFactoriesLoader从spring.factories中加载的ApplicationContextInitializer实例有以下这些。
# /spring-boot-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
# 从配置属性context.initializer.classes加载ApplicationContextInitializer实例
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
# /spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
在ConfigurableApplicationContext的refresh方法被调用之前,用于初始化ConfigurableApplicationContext实例的回调接口,这些ApplicationContextInitializer在ConfigurableApplicationContext实例被创建之后执行。
ApplicationListener
使用SpringFactoriesLoader从spring.factories中加载的ApplicationListener实例有以下这些。
# /spring-boot-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
# /spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
基于java java.util.EventListener接口的观察者模式。用于处理Spring容器中的ApplicationEvent事件。
后面会着重说明ConfigFileApplicationListener类。
可以自己实现ApplicationContextInitializer、ApplicationListener并将其配置到spring.factories文件中来实现对Spring Boot应用的定制。
run方法
这个run方法直指SpringApplication实例的的(String… args)方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
//SpringApplication实例的run方法的监听器。从spring.factories加载并实例化所有SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类
//目前为止spring.factories中配置的SpringApplicationRunListener的实现只有EventPublishingRunListener,并且也仅有这一个实现类
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@1999} size = 4
// 0 = {LoggingApplicationListener@2009}
// 1 = {BackgroundPreinitializer@2010}
// 2 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@2011} 从配置项context.listener.classes加载并实例化ApplicationListener,然后对当前事件做处理
// 3 = {LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener@2012}
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//创建environment并调用EnvironmentPostProcessor#postProcessEnvironment进行配置文件读取
//ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//根据this.webApplicationType加载并实例化对应的ApplicationContext实现类
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//调用ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize
//将MainApp注册到BeanFactory
//发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//调用AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
refreshContext(context);
//空方法,子类可以充重写来扩展功能
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//ApplicationStartedEvent
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@6652} size = 2
// 0 = {BackgroundPreinitializer@6657}
// 1 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@6658}
listeners.started(context);
//调用ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner的run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@6676} size = 3
// 0 = {BackgroundPreinitializer@6667}
// 1 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@6546}
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
以下将重点说明该方法的三处代码
- SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
- ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
- context = createApplicationContext();
- prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
- refreshContext(context);
- afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
- listeners.started(context);
- callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
- listeners.running(context);
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
从spring.factories中加载并实例化接口SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类,如下
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
目前为止,接口SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类只有一个,就是EventPublishingRunListener。
Spring Boot要求,SpringApplicationRunListener的实现必须有一个接受SpringApplication application, String[] args两个参数的构造器。看EventPublishingRunListener的构造器。
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
在这里,构造SpringApplication时从spring.factories文件加载的ApplicationListener都被添加到EventPublishingRunListener的initialMulticaster属性中去了。
类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster在refresh时还会用到。它的作用就相当于是一系列ApplicationListener的代理,当有事件发生时,直接发送给ApplicationEventMulticaster就行。
事件都将通过SpringApplicationRunListeners实例来发布。
- ApplicationStartingEvent、ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent、ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent、ApplicationPreparedEvent事件会借助EventPublishingRunListener来发布。
- ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent事件却是使用ApplicationContext发布。
可以自己实现SpringApplicationRunListener并将其配置到spring.factories中来实现对SpringApplication的run方法的监听。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// TODO
创建并初始化ConfigurableEnvironment实例,之后发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件来调用相应的ApplicationListener对ConfigurableEnvironment实例做进一步的处理。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@2170} size = 7
// 0 = {ConfigFileApplicationListener@2176} 从spring.factories中加载并实例化EnvironmentPostProcessor,自身也是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor的实现。对这些EnvironmentPostProcessor排序,然后调用EnvironmentPostProcessor#postProcessEnvironment方法。
// 1 = {AnsiOutputApplicationListener@2177}
// 2 = {LoggingApplicationListener@2178}
// 3 = {ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener@2179}
// 4 = {BackgroundPreinitializer@2180}
// 5 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@2181}
// 6 = {FileEncodingApplicationListener@2182}
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
这里看下org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener这个类,它处理ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent和ApplicationPreparedEvent两个事件。
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件完成了配置文件的加载
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 使用SpringFactoriesLoader从spring.factories中加载值为org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor的属性并实例化这些类
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
// this也是EnvironmentPostProcessor的实现
postProcessors.add(this);
//对postProcessors排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
//调用这些postProcessors的postProcessEnvironment方法
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(),
event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
它从spring.factories中加载了这些了类的实例
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
# 云环境、未配置,不会执行这个类
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
# 处理json格式的配置,
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
# 处理系统环境变量
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
三者顺序:SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor、SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor、ConfigFileApplicationListener
主要看ConfigFileApplicationListener实现的EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment方法
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
其最关键的是最后一句代码
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
Loader类实现了配置文件的加载。
-
从spring.factories中加载PropertySourceLoader的实现类并实例化这些类
# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader这里加载了两个类实例
- PropertiesPropertySourceLoader:用于加载.properties、.xml扩展名的配置文件
- YamlPropertySourceLoader:用于加载.yml、.yaml扩展名的配置文件
-
读取配置文件的位置
如果属性spring.config.location有值,则从该属性的值解析出配置文件的位置 否则从属性spring.config.additional-location的值解析出的配置文件的位置、 classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/作为配置文件的位置
-
使用PropertySourceLoader实例从上述的位置加载配置
它将配置文件封装为PropertySource并添加到当前Environment实例的propertySources中。
context = createApplicationContext();
这里创建了ApplicationContext实例,其实是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的实例。 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的无参构造器及其父类GenericApplicationContext的无参构造器
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的父类GenericApplicationContext持有一个DefaultListableBeanFactory实例。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext和DefaultListableBeanFactory这两个类都实现了几个相同的接口: BeanDefinitionRegistry、HierarchicalBeanFactory、ListableBeanFactory、BeanFactory
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);没什么好说的,这个用于扫描classpath下被@Component、@Repository、@Service、@Controller、@ManagedBean、@Named注解的类并注册到beanFactory。
这里看下this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);,以编程的方式完成被注解的类的注册。
跟踪这行代码到AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
最终发现这里注册了以下几个bean注册到beanFactory实例。
| bean name | bean class | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor | ConfigurationClassPostProcessor | 启动时处理@Configuration |
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor | AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 处理@Autowired、@Value,支持@javax.inject.Inject |
| org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor | CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 处理javax.annotation包下的注解,@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource、@WebServiceRef、@EJB |
| org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor | EventListenerMethodProcessor | 处理@EventListener |
| org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory | DefaultEventListenerFactory | 处理@EventListener |
其中,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现,同时也实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的实现。
后面refresh时会用到这几个类。
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//调用ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize
applyInitializers(context);
//无用
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
// 注册applicationArguments到BeanFactory
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//将MainApp注册到BeanFactory
//使用BeanDefinitionLoader将MainApp实例添加到BeanFactory
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//将SpringApplication中的ApplicationListener实例添加到ApplicationContext中
//发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@4303} size = 4
// 0 = {ConfigFileApplicationListener@2176}
// 1 = {LoggingApplicationListener@2178}
// 2 = {BackgroundPreinitializer@2180}
// 3 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@2181}
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
目前为止事件的发布都是使用的EventPublishingRunListener#initialMulticaster来进行的。 后面的事件发布都是用AbstractApplicationContext#applicationEventMulticaster来进行。 实际上,这两个属性是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的不同实例。
refreshContext(context);
调用了((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();,后面再说这个。
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
这个方法没有做任何事情,子类可以重写该方法。
listeners.started(context);
发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
在ApplicationStarted之后,调用ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner的run方法,用户可以自己实现这两个接口来做一些事情。
listeners.running(context);
发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件
AbstractApplicationContext
refresh方法是在AbstractApplicationContext中实现的。 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的继承体系,只列出了几个类,接口没有列出。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext
DefaultResourceLoader
看看refresh方法的实现。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 空方法,子类可以复写该方法对ApplicationContext进行扩展
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 组件扫描、注册
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 国际化
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化applicationEventMulticaster
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 空方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册Listener,ApplicationListener实例添加到applicationEventMulticaster
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 没有被@Lazy注解的bean的创建
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// ContextRefreshedEvent
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@6536} size = 5
// 0 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@6546}
// 1 = {ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener$ConditionEvaluationReportListener@6547}
// 2 = {ClearCachesApplicationListener@6548}
// 3 = {SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer$SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean@6549}
// 4 = {ResourceUrlProvider@6550}
// ServletWebServerInitializedEvent
//getApplicationListeners(event, type) = {ArrayList@6640} size = 3
// 0 = {DelegatingApplicationListener@6546}
// 1 = {ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter@6642} "public void org.springframework.boot.admin.SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar.onWebServerInitializedEvent(org.springframework.boot.web.context.WebServerInitializedEvent)"
// 2 = {ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer@6643}
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
该方法在AbstractApplicationContext中并没有实现。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
到这个方法之前,context内一共有以下以三个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现; ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor implements PriorityOrdered, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 打印警告日志 CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered 设置beanName为org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor的bean definition的的属性 PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered
beanFactory内有一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor ,同时ConfigurationClassPostProcessor也是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware
跟踪代码到PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,其中beanFactory参数就是context内那个,beanFactoryPostProcessors是上面说的context内那三个。
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
// DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 实际上,这里只有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,用于组件扫描、注册
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 实际上这里啥也没调用
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
// 实际上这里啥也没调用
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// registryProcessors = {ArrayList@3344} size = 3
// 0 = {ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer$ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor@4202}
// 1 = {SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer$CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor@4203}
// 2 = {ConfigurationClassPostProcessor@4204} 为运行时使用CGLIB增强Configuration类做准备
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
// regularPostProcessors = {ArrayList@3343} size = 1
// 0 = {ConfigFileApplicationListener$PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor@4206} reorder PropertySource
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//priorityOrderedPostProcessors = {ArrayList@4373} size = 1
//0 = {PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer@4378} 处理 ${...}
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 啥也没调用
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
//nonOrderedPostProcessors = {ArrayList@4398} size = 2
//0 = {ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetadata@4402}
//1 = {ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration$PreserveErrorControllerTargetClassPostProcessor@4403}
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
bean的加载实际上是在第一次调用invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法是进行的,这个方法内部调用了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry。 接续跟踪代码,找到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
// configCandidates内只有一个BeanDefinitionHolder,那就是MainApp了
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
// 用于解析被@Configuration注解的类
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
// 这里对MainApp进行解析
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
// 这里处理从MainApp解析出来的ConfigurationClass
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
ConfigurationClassParser#parse
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new LinkedList<>();
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
// 这里处理MainApp
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
processDeferredImportSelectors();
}
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
// 处理嵌套,递归
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.warn("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
// 处理@ComponentScan注解,进行包内组件的扫描
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
// 组件扫描
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
// 如果也是Configuration,调用parse,递归
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// Process any @Import annotations
// TODO
// 处理@Import注解,递归
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
// 处理@ImportResource注解
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// Process individual @Bean methods
// 处理@Bean方法
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
// 处理接口的default方法
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
// 处理父接口
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
各种递归啊,自己玩吧。狗带。
ConfigurationClassParser:处理@Configuration的类
处理嵌套的类 处理@PropertySources、@PropertySource 处理@ComponentScans、@ComponentScan 使用ComponentScanAnnotationParser 使用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 处理@Import 处理@ImportResource 处理@Bean
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader:处理@Configuration类本身及从ConfigurationClassParser得到的@Bean方法
看看下面这些注解的定义
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
//自动配置 AutoConfigurationImportSelector/ImportAutoConfigurationImportSelector
// 从spring.factories中加载org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的值并把他们作为Configuration类进行处理
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
完成非@Lazy的创建
调用beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); —» getBean —» doGetBean
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
//尝试获取以创建的bean对象,或者使用ObjectFactory创建bean对象
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 这里为空???
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//创建单例bean
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
获取已创建的单例bean
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
—» getSingleton(beanName, true);
this.singletonObjects: 已创建的单例bean this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation:正在创建的beanName集合 this.earlySingletonObjects:由于循环依赖而被提前创建出来的单例bean this.singletonFactories:用于创建bean的ObjectFactory
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
创建单例bean
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
//记录当前beanName到singletonsCurrentlyInCreation,表示bean正在被创建
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
//创建bean,实际上是调用了createBean方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
//从singletonsCurrentlyInCreation删除beanName,表示bean已创建
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
// 如果是新创建的单例bean
if (newSingleton) {
//this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
//this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
//this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
//this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
// 创建bean
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 应用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation
// 调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
//在这里才真正的创建bean实例
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//使用factory-method、构造器等创建bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
//每个单例bean创建时都需要经过这里
//this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
//this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
//this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
//getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//填充bean、属性赋值,如果依赖其它bean,递归调用getBean方法
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//处理Aware
//调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
//处理InitializingBean
//处理init-method
//调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
循环依赖
以两个互相依赖的单例bean ServiceA和ServiceB为例。
get a
this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(a)
this.singletonFactories.put(a, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(a);
this.registeredSingletons.add(a);
处理依赖
get b
this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(b)
this.singletonFactories.put(b, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(b);
this.registeredSingletons.add(b);
处理依赖
get a
a = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName).get();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(a, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(a);
<<---
this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(b)
this.singletonObjects.put(b, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(b);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(b);
this.registeredSingletons.add(b);
<<---
this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.remove(a)
this.singletonObjects.put(a, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(a);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(a);
this.registeredSingletons.add(a);
总结
-
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration,处理自动配置,在其上使用@Import了导入了一个ImportSelector的实现类AutoConfigurationImportSelector,用来处理spring.factories中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration属性,然后将这个属性的值作为配置类进行处理。
-
ApplicationContextInitializer,用于初始化ApplicationContext实例,将它的实现类以org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer为key配置在spring.factories中。 DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer从配置属性context.initializer.classes中加载ApplicationContextInitializer的实例并使用这些实例对ApplicationContext实例进行初始化。
3. ApplicationListener,用于Application的事件监听,ConfigFileApplicationListener用于加载配置文件。
4. AbstractApplicationContext,整个Spring应用的上下文。
5. BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用于对Spring应用中的bean definitions修改。 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的一个实现,处理配置类的加载解析。
6. BeanPostProcessor,用于对Spring应用中new bean instance的修改,如生成代理等。AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的实现,用于对@Autowired、@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource的处理。